Selecting the right low voltage current transformer means focusing on accuracy, insulation, thermal performance, and mechanical strength. Each specification affects performance, safety, and cost. For example, higher accuracy classes reduce errors but may increase costs, while robust insulation and mounting options protect equipment in demanding settings. Maliotech’s LMZ Series demonstrates these qualities, offering high precision and flexible installation. In real-world scenarios, matching transformer specifications to your application ensures reliable operation and long-term value.
Low Voltage Current Transformer Basics
Choosing the right low voltage current transformer starts with understanding a few key specifications. These include the primary and secondary current ratings, the transformation ratio, and the accuracy class. Each of these factors plays a major role in how well the transformer will perform in your application.

Primary and Secondary Current Ratings
The primary current rating tells you the maximum current the transformer can handle on the input side. The secondary current rating is the output current that the transformer delivers to measuring or protection devices. Most low voltage current transformers have a standardized secondary current of either 1 ampere or 5 amperes. This standardization helps ensure compatibility with meters and relays.
- Typical secondary current ratings:
- 1 ampere (A)
- 5 amperes (A)
Selecting the correct primary and secondary current ratings is important for both performance and safety. If the ratings do not match your system, several problems can occur:
- Inaccurate measurements can affect the entire installation.
- Overloading may cause core saturation, which increases measurement errors and shortens the transformer's life.
- Insulation failure can lead to excessive heat, risking damage or even explosions.
- An open secondary circuit can create dangerously high voltages, which may cause electric shock, arcs, or fires.
Tip: Always match the transformer's current ratings to your system's requirements to avoid these risks.
The Maliotech LMZ Series offers secondary current options of 1A and 5A, making it flexible for different setups. Its robust design ensures safe operation even in demanding environments.
Transformation Ratio and Accuracy Class
The transformation ratio is the relationship between the primary and secondary currents. For example, a ratio of 100:5 means that when 100A flows through the primary, 5A will flow through the secondary. This ratio must match the needs of your measuring or protection devices.
Accuracy class is another critical specification. It tells you how closely the transformer’s output matches the true value of the current. International standards like IEC and ANSI define common accuracy classes:
| Standard | Accuracy Class |
|---|---|
| ANSI | 0.3, 0.6, 1.2 |
| IEC | 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 1 |
Accuracy class matters because it affects how well the transformer performs in different applications:
- Metering accuracy classes are designed for high precision. These are essential for billing and monitoring, where even small errors can have big impacts.
- Protection accuracy classes can tolerate larger errors but are crucial for reliable operation during faults.
- Metering accuracy transformers are highly accurate across a range of currents, making them suitable for utility billing.
- Relay accuracy transformers are less precise but work effectively over a broader current range.
- The accuracy class defines how much the secondary current can differ from the expected value based on the transformation ratio.
The Maliotech LMZ Series stands out for its high accuracy, making it a strong choice for both metering and protection tasks. Its precision ensures reliable measurements, which is vital for energy management and system safety.
Note: Always check the required accuracy class for your application before selecting a transformer.
A good understanding of these basic specifications will help you choose the right low voltage current transformer for your needs.
Installation and Environmental Considerations
Mounting Options and Physical Form
The way a current transformer is built affects how and where it can be installed. Some transformers have a solid-core design, which means the conductor must be disconnected before installation. Others use a split-core or clamp-on style, making them easier to install around existing wires. The table below compares these types:
| Type | Description | Best For | Accuracy Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-Core (Toroidal) | Requires disconnection for install | New installations, high accuracy | Highest accuracy |
| Split-Core | Opens for installation | Retrofit, energized systems | Slightly higher error (air gaps) |
| Clamp-On (Portable) | Temporary measurement | Troubleshooting | Not for permanent metering |
Split-core transformers are popular for upgrades because they fit around wires without disconnecting power. This reduces downtime and saves money. The Maliotech LMZ Series supports both vertical and horizontal mounting, which gives installers more options in tight spaces.
Insulation, Voltage Class, and Frequency
Insulation protects the transformer from electrical faults and harsh environments. Different insulation classes use different materials and have different temperature limits. The chart below shows how insulation classes compare by maximum operating temperature:
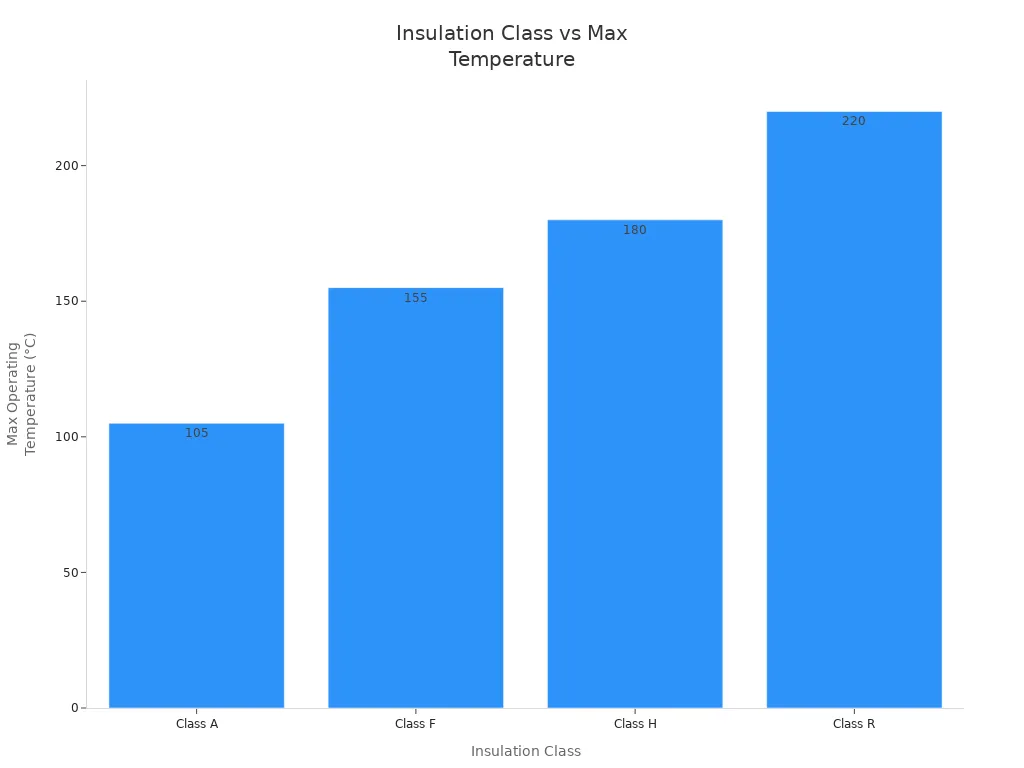
For low voltage current transformers, Class F insulation is common. It uses epoxy resin or polyester and can handle up to 155°C. The Maliotech LMZ Series is rated for insulation voltages up to 3kV for 60 seconds, which helps keep systems safe.
Most low voltage current transformers work at 50 or 60Hz. Using them at higher frequencies can cause losses and reduce accuracy. The LMZ Series is designed for standard power system frequencies, which ensures reliable performance.
Temperature and Humidity Ratings
Environmental conditions can affect transformer performance. High temperatures may increase losses and lower accuracy. Humidity can lead to insulation problems. The Maliotech LMZ Series operates in temperatures from -5°C to +40°C and can handle up to 80% relative humidity. It is also suitable for locations below 1000 meters in altitude. These ratings make it a strong choice for many indoor and sheltered outdoor applications.
Tip: Always check the temperature and humidity ratings before installing a transformer. This helps prevent failures and extends the life of your equipment.
Application and Compliance
Metering, Protection, and Monitoring Uses
A Low Voltage Current Transformer serves many roles in electrical systems. Choosing the right type depends on the specific application. Each use case has unique requirements for accuracy, durability, and installation.
- Distribution Panels and Switchgear: These transformers provide real-time current monitoring and help protect circuits from overloads.
- Industrial Automation: They ensure safe operation of motors and heavy machinery by tracking current flow.
- Commercial Buildings: Energy management systems use them to monitor load distribution and optimize power usage.
- EV Charging Stations: They measure energy consumption and support smart grid functions.
For metering, high accuracy is essential. Protection applications focus on reliability during faults. Monitoring uses may prioritize flexibility and ease of installation. The Maliotech LMZ Series adapts well to all these scenarios, offering both precision and robust construction.
Tip: Always match the transformer’s features to your application to ensure safety and performance.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Compliance with international standards is critical when selecting a Low Voltage Current Transformer. These standards guarantee measurement accuracy, system safety, and long-term reliability.
| IEC Standard | Focus Area | Description / Application |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 60076-1 | General requirements | Core design, nameplate data, tolerances |
| IEC 60076-2 | Temperature rise | Limits and measurement methods |
| IEC 60076-3 | Dielectric tests | Lightning and switching impulse levels |
| IEC 60076-5 | Short-circuit withstand | Mechanical strength and design validation |
| IEC 60076-10 | Sound level | Acoustic emissions under load |
| IEC 60076-20 | Eco-design | Efficiency and environmental performance |
Standards like IEC 61869 and UL 2808 set strict rules for accuracy, burden, and construction. Following these standards helps prevent measurement errors and safety hazards. A mismatched transformer can cause errors, false trips, or even compromise system safety.
Note: Always check that your transformer meets the latest standards for your region and application.
Common Mistakes in Selection

Overlooking Key Specifications
Many engineers and buyers make mistakes by not paying close attention to important transformer specifications. These errors can lead to serious problems in electrical systems. Some of the most common mistakes include:
- Selecting the wrong current transformer ratio, which can cause inaccurate measurements.
- Choosing a primary rating that does not match the system’s normal operating current, leading to errors or even transformer saturation.
- Using a CT ratio that is too low, which may result in the transformer core saturating and producing unusable meter readings.
- Picking a CT ratio that is too high, which can make the secondary output too small and reduce measurement accuracy.
- Failing to select a ratio where the normal operating current is about 60–90% of the CT’s primary rating.
Tip: Always check that the transformer’s current ratings match your system’s needs. This helps prevent overheating, inaccurate readings, and safety hazards.
Some key specifications are often neglected. The table below highlights these and explains why they matter:
| Specification | Importance |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | Mismatched voltage can cause inefficiency and overheating. |
| Frequency | Using the wrong frequency affects performance. |
| Vector Group Compatibility | Incorrect vector group can disrupt parallel operation. |
| Impedance | Impacts voltage regulation and system safety. |
| Cooling Method | Influences installation and overload capability. |
| Insulation Class | Affects lifespan and resistance to temperature rise. |
The Maliotech LMZ Series makes it easier to avoid these mistakes. Clear terminal markings (P1, P2, S1, S2) and detailed documentation help ensure correct installation and operation.
Ignoring Environmental or Application Needs
Ignoring the environment or the specific application can shorten transformer life and cause failures. Transformers must handle electrical loads and withstand environmental conditions. If these factors are ignored, problems like insulation failure or breakdowns can occur.
Common environmental risks include:
- High humidity, which can cause corrosion and insulation breakdown.
- Dust buildup, which blocks cooling and raises temperatures.
- Vibration, which stresses parts and damages insulation.
Other factors to consider:
- Temperature extremes
- Humidity
- Altitude
- Air pollution
- Seismic activity
- UV exposure
- Salt fog (near coasts)
- Flooding risk
Best Practice: Always review the installation site’s conditions. The Maliotech LMZ Series is rated for a wide range of temperatures and humidity, making it suitable for many environments. Following manufacturer guidelines and keeping components clean and dry will help prevent common issues.
Choosing the right low voltage current transformer means checking key specifications. The table below highlights the most important ones:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 0.5kV, 0.66kV |
| Secondary Current | 5A, 1A |
| Installation Method | Vertical or horizontal |
| Insulation Withstand Voltage | 3kV/60s |
| Frequency | 50 or 60Hz |
Matching these features to your application improves safety, accuracy, and equipment life. For expert advice and reliable solutions, consult manufacturers like Maliotech. Their support and clear product design help ensure success in any setting.
FAQ
What is a low voltage current transformer used for?
A low voltage current transformer measures electrical current in power systems. It helps monitor energy use, protect equipment, and ensure safe operation. Many industries use these transformers in panels, switchgear, and energy management systems.
How do I choose the right current ratio?
Select a current ratio that matches your system’s normal operating current. The primary rating should be about 60–90% of your typical load. This ensures accurate readings and prevents transformer saturation.
Can I install the LMZ Series transformer outdoors?
The LMZ Series works best in indoor or sheltered locations. It handles temperatures from -5°C to +40°C and up to 80% humidity. For outdoor use, always provide protection from direct rain and harsh weather.
What do the terminal markings P1, P2, S1, and S2 mean?
| Terminal | Function |
|---|---|
| P1, P2 | Primary polarity ends |
| S1, S2 | Secondary polarity ends |
Always connect terminals as shown in the manual for correct operation.
Post time: Feb-05-2026

